ELF binary size information#
Individual size information#
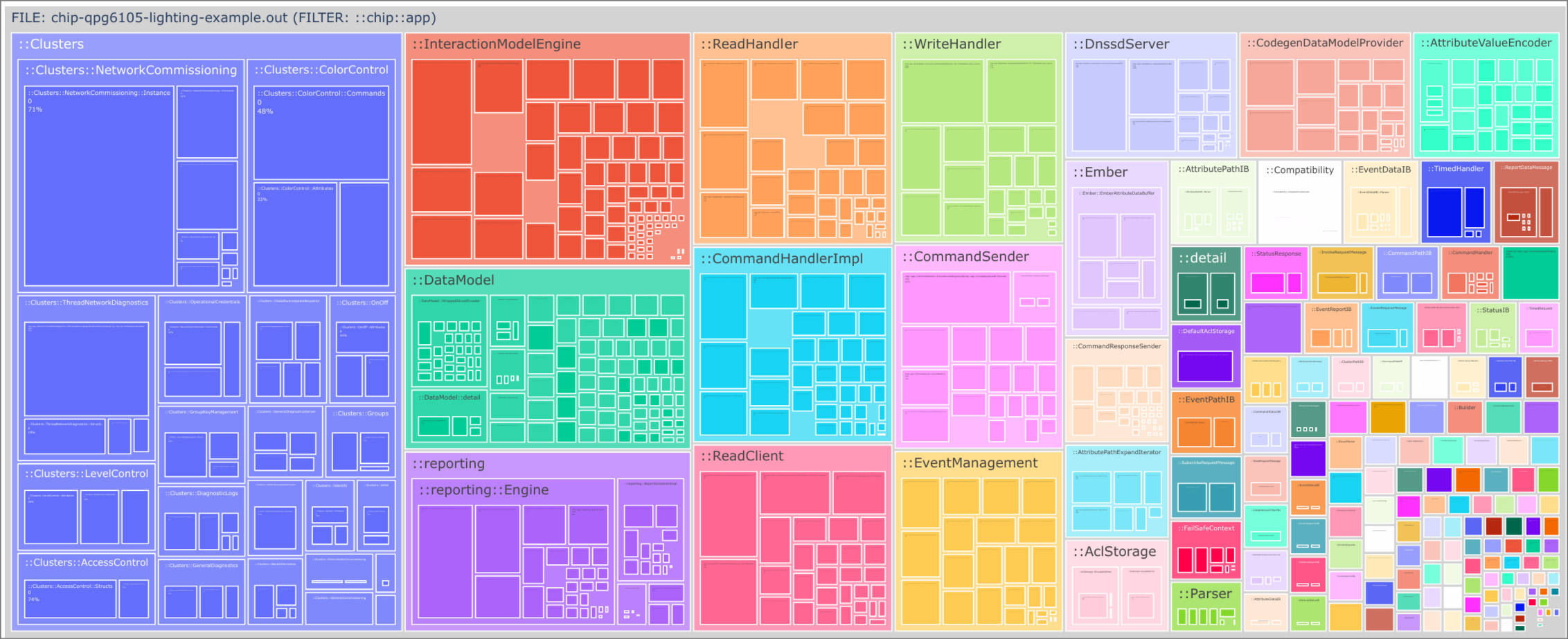
file_size_from_nm.py is able to build an interactive tree map of
methods/namespaces sizes within an elf binary.
Use it to determine how much space specific parts of the code take. For example:
./scripts/tools/file_size_from_nm.py \
--zoom '::chip::app' \
./out/qpg-qpg6200-light/chip-qpg6200-lighting-example.out
could result in a graph like:
Determine difference between two binaries#
binary_elf_size_diff provides the ability to compare two elf files. Usually
you can build the master branch of a binary and save it somewhere like
./out/master.elf and then re-build with changes and compare.
Example runs:
> ./scripts/tools/binary_elf_size_diff.py \
./out/qpg-qpg6200-light/chip-qpg6200-lighting-example.out \
./out/qpg-master.out
Type Size Function
------- ------ -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
CHANGED -128 chip::app::CodegenDataModelProvider::WriteAttribute(chip::app::DataModel::WriteAttributeRequest const&, chip::app::A...
CHANGED -76 chip::app::InteractionModelEngine::CheckCommandExistence(chip::app::ConcreteCommandPath const&, chip::app::DataModel...
CHANGED -74 chip::app::reporting::Engine::CheckAccessDeniedEventPaths(chip::TLV::TLVWriter&, bool&, chip::app::ReadHandler*)
REMOVED -58 chip::app::DataModel::EndpointFinder::EndpointFinder(chip::app::DataModel::ProviderMetadataTree*)
REMOVED -44 chip::app::DataModel::EndpointFinder::Find(unsigned short)
CHANGED 18 chip::app::WriteHandler::WriteClusterData(chip::Access::SubjectDescriptor const&, chip::app::ConcreteDataAttributePa...
ADDED 104 chip::app::DataModel::ValidateClusterPath(chip::app::DataModel::ProviderMetadataTree*, chip::app::ConcreteClusterPat...
ADDED 224 chip::app::WriteHandler::CheckWriteAllowed(chip::Access::SubjectDescriptor const&, chip::app::ConcreteDataAttributeP...
TOTAL -34
> ./scripts/tools/binary_elf_size_diff.py \
--output csv --skip-total \
./out/qpg-qpg6200-light/chip-qpg6200-lighting-example.out ./out/qpg-master.out
Type,Size,Function
CHANGED,-128,"chip::app::CodegenDataModelProvider::WriteAttribute(chip::app::DataModel::WriteAttributeRequest const&, chip::app::AttributeValueDecoder&)"
CHANGED,-76,"chip::app::InteractionModelEngine::CheckCommandExistence(chip::app::ConcreteCommandPath const&, chip::app::DataModel::AcceptedCommandEntry&)"
CHANGED,-74,"chip::app::reporting::Engine::CheckAccessDeniedEventPaths(chip::TLV::TLVWriter&, bool&, chip::app::ReadHandler*)"
REMOVED,-58,chip::app::DataModel::EndpointFinder::EndpointFinder(chip::app::DataModel::ProviderMetadataTree*)
REMOVED,-44,chip::app::DataModel::EndpointFinder::Find(unsigned short)
CHANGED,18,"chip::app::WriteHandler::WriteClusterData(chip::Access::SubjectDescriptor const&, chip::app::ConcreteDataAttributePath const&, chip::TLV::TLVReader&)"
ADDED,104,"chip::app::DataModel::ValidateClusterPath(chip::app::DataModel::ProviderMetadataTree*, chip::app::ConcreteClusterPath const&, chip::Protocols::InteractionModel::Status)"
ADDED,224,"chip::app::WriteHandler::CheckWriteAllowed(chip::Access::SubjectDescriptor const&, chip::app::ConcreteDataAttributePath const&)"
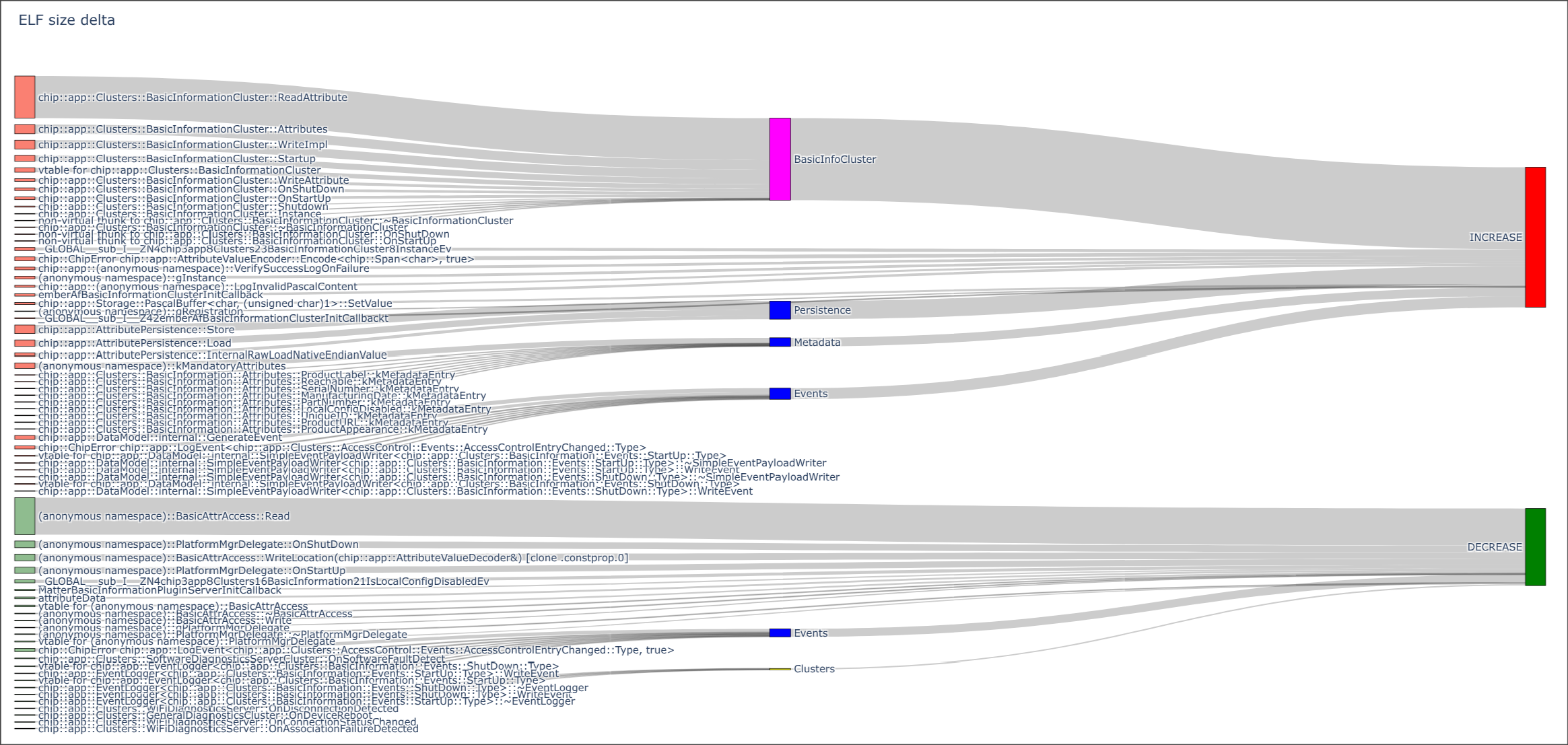
The diff can also export a sankey data for the differences. Example run:
# Running via `uv` from https://github.com/astral-sh/uv ensures packages are loaded and is generally fast
# sankey-rules are optional and are of the form:
# match "<regex>" to <group_name> "color" colorstr
# where the color part is optional
#
# Example used rules.txt:
#
# match "::k(MetadataEntry|MandatoryAttributes)" to "Metadata"
# match "chip::app::Clusters::BasicInformationCluster" to "BasicInfoCluster" color magenta
# match "AttributePersistence" to Persistence
# match "Event" to Events color blue
# match "chip::app::Clusters::" to Clusters color yellow
#
uv run --script ./scripts/tools/binary_elf_size_diff.py \
out/branch-builds/migrate_basic_info_to_code/stm32-stm32wb5mm-dk-light/chip-stm32-lighting-example.elf \
out/branch-builds/better_scripts/stm32-stm32wb5mm-dk-light/chip-stm32-lighting-example.elf \
--output sankey \
--sankey-rules out/rules.txt
Looking at assembly code#
For general tests, the Godbolt compiler explorer is a great resource.
Locally running compiler explorer#
There are cases where you may want to investigate how CHIP code is compiled and the CHIP include/build options can be quite complex. In this case, you can run the compiler explorer from source locally using the following instructions:
install node 20 or above (if you do not have it installed yet)
compile compiler-explorer from source
Set up a local C++ config in
etc/config/c++.local.properties, oftengcc-arm-none-eabi-g++as a compileradd the relevant compiler settings:
compile a sample application using the relevant variant. For example
./scripts/build/build_examples.py --target efr32-brd2703a-lock buildThis will create a compile_commands.json that contains compiler arguments to compile files. We have a tool
compile_flags_from_compile_commands.pyto extract relevant compile flags.
The following instructions should work on a chip-build-vscode image. Set the
port accordingly (default is 10240)
# Install NVM to get node modules available
curl -o- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nvm-sh/nvm/v0.40.3/install.sh | bash
source ~/.bashrc
# Install Node 22 (20 is minimum required, newer is better)
nvm install 22
nvm use 22
# for the compiler path for arm-none-eabi-g++ to be correct, this may be needed
source scripts/activate
# Checkout compiler explorer and build
git clone https://github.com/compiler-explorer/compiler-explorer.git out/compiler-explorer
cd out/compiler-explorer
# generate a relevant config file, like:
echo "compilers=gcc-arm-none-eabi-g++" >etc/config/c++.local.properties
echo "compiler.gcc-arm-none-eabi-g++.name=arm-none-eabi-g++" >>etc/config/c++.local.properties
echo "compiler.gcc-arm-none-eabi-g++.exe=arm-none-eabi-g++" >>etc/config/c++.local.properties
# Build and run, ready for testing
make EXTRA_ARGS="--language c++ --port 8000"
You can get compile flags (generally include paths are important) via
scripts/tools/compile_flags_from_compile_commands.py. Here is an example
invocation
scripts/tools/compile_flags_from_compile_commands.py \
-c out/efr32-brd2703a-lock/compile_commands.json \
flags basic-information \
| wl-copy
# NOTE: could also use `xclip -selection clipboard` for X11 systems
You may want to enable highlighting via More->Settings and have:
Site theme (as applicable)
Line highlighting color scheme as Rainbow (clearer code as opposed to just gray scale)